Right Now
Understanding Hydroquinone: The Controversial
Skin-Lightening Agent and Its Industrial Applications
the
molecular formula C6H6O2. Its structure consists of a benzene ring substituted
with two hydroxyl groups at para positions. At room temperature, it appears as
white crystalline solid with a slight characteristic odor. The compound is
moderately soluble in water and highly soluble in organic solvents like ethanol
and ether. Its molecular weight is 110.11 g/mol, and it has a melting point of
172°C. These physical and chemical properties make it versatile for various
applications across different industries.
Medical and Cosmetic Applications
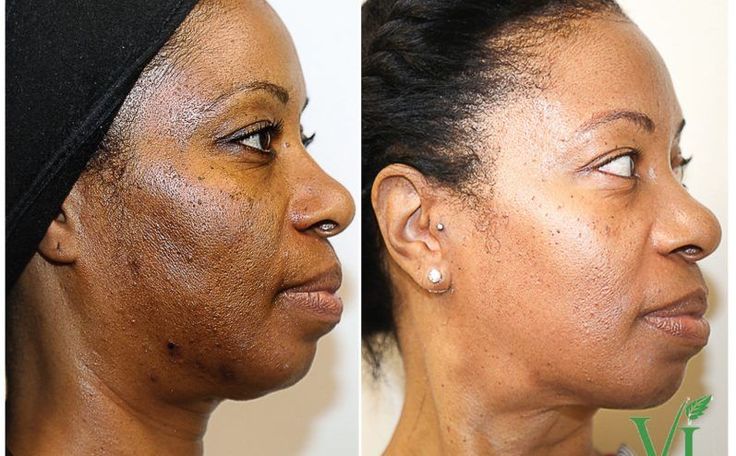
In the medical and cosmetic fields, Hydroquinone
has gained significant attention as a skin-lightening agent. It works by
inhibiting tyrosinase, the enzyme responsible for melanin production in skin
cells. This mechanism effectively reduces hyperpigmentation, age spots, and
melasma. The compound is typically used in concentrations ranging from 2% to 4%
in prescription formulations, while over-the-counter products usually contain
lower concentrations. However, its use in cosmetics has become increasingly
controversial due to potential side effects and safety concerns, leading to
restrictions or bans in several countries, particularly in the European Union.
Get
More Insights On- Hydroquinone
More Posts

Report This Post
Please complete the following requested information to flag this post and report abuse, or offensive content. Your report will be reviewed within 24 hours. We will take appropriate action as described in Findit terms of use.